
Introduction: Why Surgical Positioning Matters
Proper surgical positioning is a critical element of patient safety and surgical success. Among the standard surgical positions, the lateral position is widely used in operations requiring side access to the thoracic cavity, kidneys, spine, or hips. Ensuring correct use of this position minimizes complications, optimizes surgical access, and improves postoperative outcomes.
This guide will explore everything you need to know about the lateral surgical position—its variations, applications, equipment, and associated risks—so you can make informed decisions about its implementation in the operating room.
What Is the Lateral Position?
The lateral position refers to the placement of a surgical patient lying on their left or right side, with the operative side facing up. This positioning provides the surgical team with lateral access to specific anatomical regions while maintaining respiratory and circulatory function.
Why Would You Place a Patient on the Left Side or Right Side?
Depending on the side of the body on which the patient is being operated, the patient will lie on their left or right side.
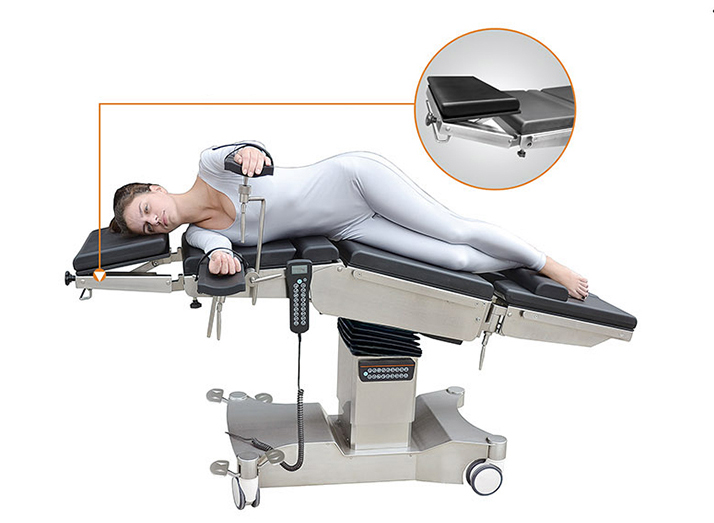
Right Lateral Position
The right lateral position is used in operations where the doctor or surgeon needs access to the left side of the patient's body. Therefore, the patient would be placed on their right side with the left side of the body facing up.
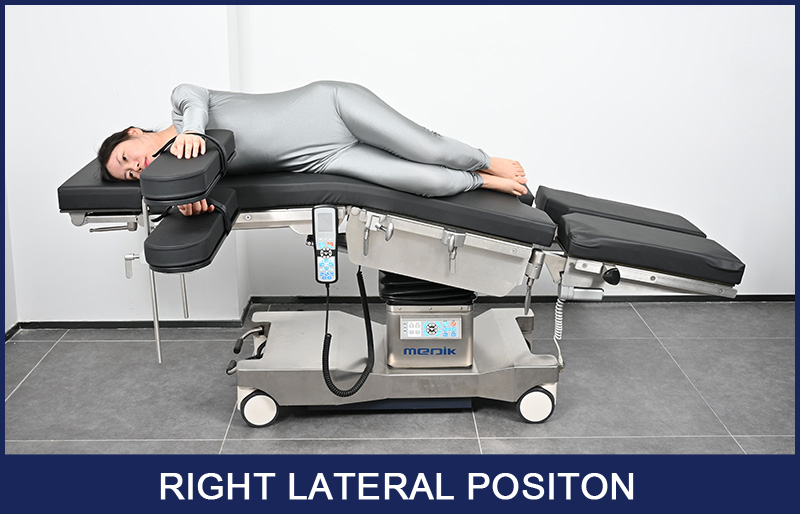
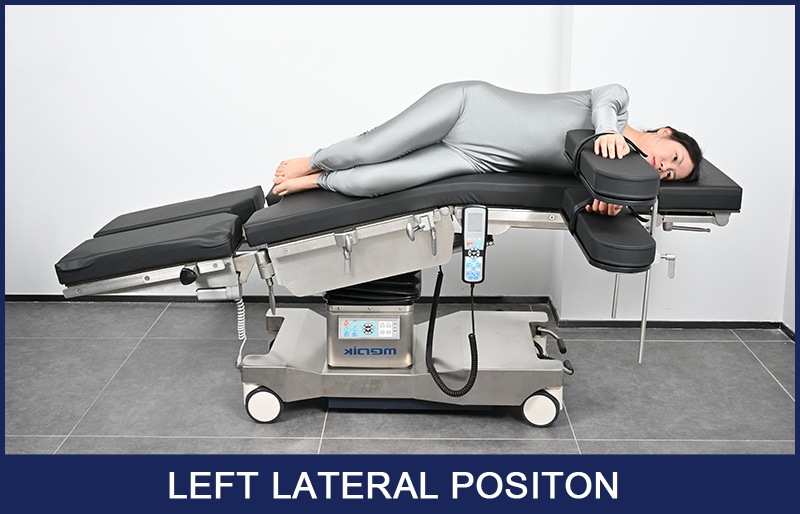
Left Lateral Position
The opposite of the right lateral position, the left lateral position is used in operations where the doctor or surgeon needs access to the right side of the patient's body. Therefore, the patient would be placed on their left side with the right side of the body facing up.
When to use Lateral Position?
The lateral position is a commonly used position in various surgical procedures. Here are some types of surgeries that may use the lateral position:
1. Kidney Surgery
Used in nephrectomies and other renal procedures. The lateral decubitus position offers unobstructed access to the retroperitoneal space.
2. Thoracic Surgery
For lung resections, thoracotomies, and pleural procedures, the lateral position allows entry into the chest cavity without compromising adjacent structures.
3. Spinal Surgery
Surgeons often use the lateral position for lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF) or other minimally invasive spinal procedures.
4. Hip Surgery
Total hip replacements and hip arthroscopies may use the lateral position for enhanced joint visualization and reduced dislocation risk.
5. Vascular Procedures
Lateral positioning is sometimes applied in femoral artery access or retroperitoneal vascular reconstructions.
Key Benefits of the Lateral Surgical Position
✅ Improved access to lateral anatomical structures
✅ Enhanced visualization for minimally invasive surgeries
✅ Better patient ventilation in certain procedures
✅ Reduced intraoperative bleeding due to gravity
✅ Facilitates fluid drainage from surgical site
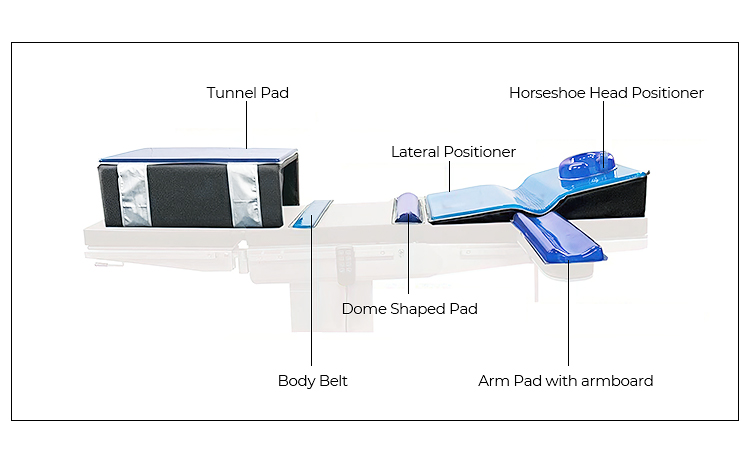
Lateral Position Supporting Devices
There are several types of padding and positioning devices commonly used to support patients in a lateral position. These devices help prevent pressure ulcers and maintain proper alignment of the spine, hips, and other joints. Some of the most common types of lateral position devices are:
* Horseshoe Head positioner – Supports the head while reducing ocular and cranial pressure.
* Multi-Posture Armboard – Maintains proper arm alignment and prevents nerve compression.
* Lateral Positioner with Axillary Support – Prevents shoulder injury and aligns the spine. Integral channels support the lower shoulder.
* Tunnel Pad – Keeps hips and legs in correct anatomical alignment; prevents skin breakdown.
* Positioning belts: Used to safely secure the patient and prevent unintended movement or falls.
Potential Complications of Lateral Positioning
Despite its advantages, improper application of the lateral position can lead to complications:
● Respiratory Issues: Reduced lung expansion, especially in obese patients.
● Cardiovascular Instability: Decreased venous return and cardiac output.
● Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Especially the brachial plexus, sciatic, and peroneal nerves.
● Ocular Injuries: Due to pressure on the dependent eye.
● Patient Movement or Falls: Inadequate securing may result in surgical delays or injury.
Mitigation Tip: Use evidence-based positioning protocols, continuous intraoperative monitoring, and staff training to reduce complication rates.
Best Practices for Lateral Positioning
● Preoperative Assessment: Evaluate comorbidities, weight, and anatomical risks.
● Device Setup: Use the correct positioning aids and test for stability.
● Team Communication: Coordinate with anesthesia, surgical, and nursing staff.
● Intraoperative Reassessment: Regularly check for pressure points or alignment issues.
● Postoperative Monitoring: Assess for nerve function and skin integrity.
Conclusion
The lateral position in surgery offers significant benefits when used appropriately, enabling better access to specific anatomical regions while supporting patient safety. However, improper technique or equipment can lead to serious complications. By understanding its uses, risks, and best practices, healthcare professionals can optimize outcomes and improve patient care quality.
Related Resources
Reference
1. Butterworth, J. F., Mackey, D. C., & Wasnick, J. D. (2018). Morgan and Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
2. Rothrock, J. C. (2019). Alexander's Care of the Patient in Surgery (16th ed.). Elsevier.
3. American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology. (2021). Patient Positioning Guidelines for Anesthesia Providers.
https://www.aana.com/docs
4. Motacki, K., & Boyle, K. (2016). A Guide to Patient Safety in the Operating Room. Springer Publishing.
5. Kwee, M. M., Ho, Y. H., & Rozen, W. M. (2015). The prone position during surgery and its complications: A systematic review and evidence-based guidelines. International Surgery, 100(2), 292–303.
https://doi.org/10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00256.1
6. Association of periOperative Registered Nurses (AORN). (2020). Guidelines for Patient Positioning.
https://www.aorn.org/guidelines
7. Pandit, J. J., & Pandit, M. (2021). Positioning in Anaesthesia and Surgery: A Practical Guide. Anaesthesia Reports, 9(1), e12048.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anr3.12048