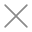

Surgical tables are the foundation of every operating room. They support patients during critical procedures and must maintain absolute reliability and safety. Like any precision medical equipment, the performance and lifespan of surgical tables depend largely on regular maintenance and proper usage. In this article, we’ll explore the key maintenance practices that extend the life of surgical tables while ensuring patient and staff safety.
1. Understanding the Lifespan of a Surgical Table
A high-quality surgical table typically lasts 10 to 15 years, depending on its build quality, frequency of use, and maintenance schedule. Tables used in high-volume operating rooms may experience more mechanical wear, requiring more frequent inspections and part replacements. Manufacturers design surgical tables to withstand years of demanding use, but neglecting preventive care can significantly reduce their functional lifespan.
2. Daily and Routine Maintenance
a. Cleaning and Disinfection
After every procedure, the table surface should be cleaned with neutral pH detergents and approved disinfectants. Avoid harsh chemicals that may corrode stainless steel or damage the table’s hydraulic or electric components. Pay close attention to joints, actuators, and movable parts—residual fluids or debris can impair movement and harbor bacteria.
b. Visual Inspection
Before each use, inspect:
- The brake system for stability.
- The hydraulic or electric controls for smooth motion.
- Any visible damage or wear to cables, pads, and connectors.
Early detection of small issues prevents costly repairs later.
3. Scheduled Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance—recommended every 6 to 12 months—should be performed by trained biomedical engineers or authorized service personnel. This includes:
- Lubricating moving joints and actuators.
- Checking hydraulic oil levels or electric motor performance.
- Calibrating control panels and safety locks.
- Replacing worn-out components like seals, bearings, and cables.
Manufacturers often provide maintenance kits and service manuals specifying part replacement intervals. Following these guidelines ensures compliance with hospital safety standards and regulatory requirements (such as IEC 60601-1).
4. Electrical and Hydraulic Safety Checks
Electric surgical tables require special attention to their power systems, including fuses, connectors, and control circuits. Any sign of overheating, unusual noise, or fluid leakage should prompt immediate service. For hydraulic tables, check for oil leaks, air in the lines, or uneven motion—these indicate potential seal or valve problems that must be corrected immediately.
5. Proper Usage and Staff Training
Even the most durable surgical table can be damaged by improper use. Medical staff should receive periodic training on:
- Weight limits and patient positioning.
- Safe adjustment procedures.
- Emergency release mechanisms.
Proper handling minimizes strain on mechanical components and ensures safe operation for both patients and clinicians.
6. When to Consider Replacement
Signs that a surgical table may need replacement include:
- Frequent breakdowns despite regular maintenance.
- Inconsistent positioning accuracy.
- Non-compliance with new safety or imaging standards.
- Excessive corrosion or worn-out actuators.
Modern surgical tables offer advanced features such as carbon fiber tabletops, remote control operation, and X-ray compatibility, which improve workflow efficiency and patient safety.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance is the most cost-effective way to protect your investment and ensure surgical safety. By implementing a consistent inspection and servicing schedule, healthcare facilities can extend the lifespan of their surgical tables while maintaining high standards of performance and hygiene.
References
1. STERIS Corporation. Surgical Table Preventive Maintenance Guidelines. 2023.
2. Hillrom (now Baxter). Operating Table Maintenance & Inspection Manual. 2022.
3. IEC 60601-1: Medical Electrical Equipment – General Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance.
4. AORN Journal. Equipment Maintenance in the Operating Room: Best Practices for Patient Safety. Vol. 116, Issue 4, 2022.